Head and Neck Cancer
Cancer : A tumour begins when healthy cells change and grow out of control, forming a mass called a tumour. A tumour can be cancerous or benign. A cancerous tumour is a malignant tumour, meaning it can grow and spread to other parts of the body. A benign tumour means the tumour can grow locally but will not spread to other areas of the body.
“Head and neck cancer” is the term used to describe several different malignant tumours that develop in or around the throat, larynx, nose, sinuses, and mouth.
Head and neck cancer are the 6th most common cancer worldwide. India accounts for 57% of the total number of cases; nearly 80,000 new cases of oral cancer are registered in the country every year. The use of smokeless tobacco in various forms like gutkha, paan masala etc is the main reason oral cancer in India.
Most head and neck cancers are squamous cell carcinomas. This type of cancer begins in the flat squamous cells that make up the thin layer of tissue on the surface of the structures in the head and neck. If a cancer is only found in the squamous layer of cells, it is called carcinoma in situ. If the cancer has grown beyond this cell layer and moved into the deeper tissue, then it is called invasive squamous cell carcinoma. If doctors cannot identify where the cancer began, it is called a cancer of unknown primary.
Types Of Head And Neck Cancer
There are 5 main types of head and neck cancer, each named according to the part of the body where they develop. For more information about a specific type, visit the guide dedicated to that type of head and neck cancer on this same website.
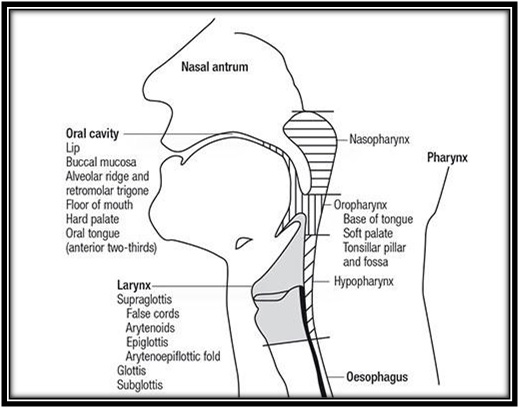
Anatomical Subsites Of Head Neck Cancer
How Does Cancer Spread in the body?
There are 4 ways that cancer spreads in the body.
Cancer can spread through tissue, the lymph system, and the blood:
Cancer may spread from where it began to other parts of the body. When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis. Cancer cells break away from where they began (the primary tumour) and travel through the lymph system or blood.
The metastatic tumour is the same type of cancer as the primary tumour. For example, if tongue cancer spreads to the lung, the cancer cells in the lung are actually tongue cancer cells.
